Phases of Project Management
The article “Key Phases of Project Management: From Initiation to Closure” explores the essential stages of successful project management. It covers initiation, planning, execution, monitoring, and closure, highlighting best practices, tools, and techniques for each phase. Aimed at project managers and professionals, it offers actionable insights to enhance efficiency, ensure project alignment with objectives, and achieve desired outcomes.
Introduction to Project Management Phases
Project management is a strategic approach that involves planning, executing, and overseeing projects to achieve specific goals. It plays a crucial role in ensuring that projects are completed on time, within budget, and to the desired quality standards. By effectively managing resources and risks, project management helps organizations to meet their objectives efficiently.
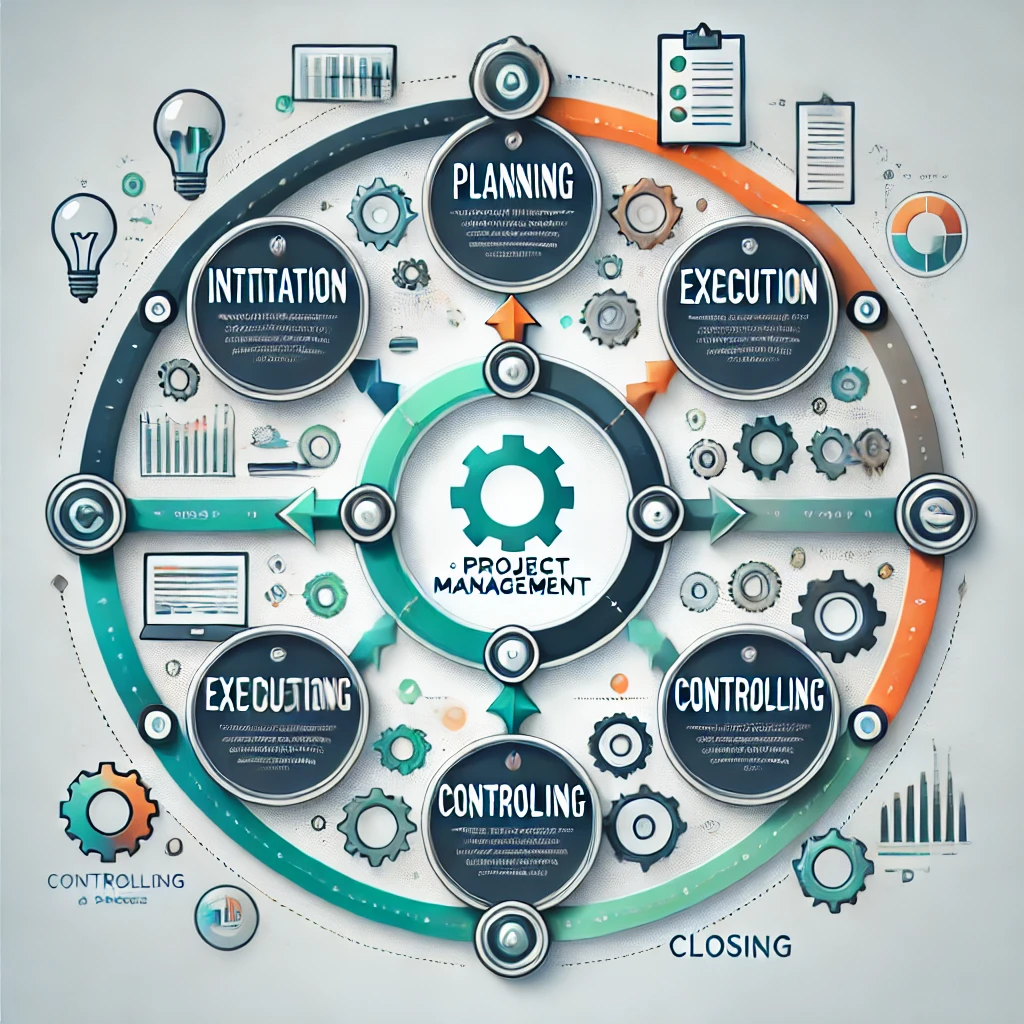
The process of project management can be broken down into several key phases: initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and controlling, and closure. Each phase serves a distinct purpose and involves specific activities that contribute to the overall success of a project. From setting the foundation in the initiation phase to wrapping up in the closure phase, understanding these stages is essential for delivering successful projects.
Initiation: Setting the Foundation
Purpose
The initiation phase is crucial as it sets the groundwork for the entire project. This is where the project’s feasibility and value are assessed. The primary goal is to ensure that the project aligns with business objectives and addresses a real need or opportunity.
Key Activities
During initiation, defining clear goals and identifying stakeholders are essential. Establishing clear objectives helps guide the project’s direction, while recognizing stakeholders ensures all voices are considered. For instance, in a new software development project, stakeholders could range from IT specialists to end-users, each bringing unique insights and requirements.
Importance
The project charter is a vital document created during this phase. It formally authorizes the project’s existence and outlines objectives, scope, and high-level deliverables. This charter acts as a reference point throughout the project lifecycle, helping to keep the team aligned and focused.
Consider a case where a company plans to launch a new product. The initiation phase would involve understanding market needs, identifying key customers, and drafting a charter that highlights the expected benefits and strategic goals. This foundational step is pivotal in steering the project toward success.
Planning: Charting the Course
Once the project is initiated, the next step is to meticulously plan every aspect. This phase is critical as 71% of projects that fail do so due to poor planning. A solid project plan acts as a roadmap, outlining tasks, timelines, and responsibilities.
Comprehensive planning involves:
- Resource allocation: Ensure that the right resources are assigned to the right tasks. This means assessing the skills of team members and matching them with project needs. It also involves budgeting and ensuring financial resources are available when needed.
- Scheduling: Creating a timeline for the project by breaking it down into phases and setting deadlines for each milestone. This helps keep the project on track and manage time effectively.
- Risk management strategies: Identify potential risks early on. Develop mitigation plans to address these risks should they arise. This proactive approach minimizes disruptions and enhances the likelihood of project success.
Effective planning is the cornerstone of a successful project, ensuring that all subsequent phases run smoothly and efficiently.
Execution: Bringing Plans to Life
Coordinating Resources
During the execution phase, the project plan is put into action. Coordinating resources and team members is crucial to ensure tasks are completed efficiently. Assigning the right tasks to the right people based on their skills and availability helps maintain momentum.
| Role | Responsibility |
|---|---|
| Project Manager | Oversees execution and manages team coordination |
| Team Member | Completes assigned tasks and collaborates with others |
| Resource Manager | Allocates resources and tracks their usage |
Tracking Progress
To stay on schedule, it’s vital to track progress and manage any changes promptly. Regular updates on milestones ensure the project stays aligned with its objectives. Flexible change management allows the team to adapt to unforeseen challenges without derailing the project.
Communication
Clear communication strategies are essential for successful execution. Regular meetings, status reports, and open channels for feedback keep everyone informed and engaged. This transparency helps prevent misunderstandings and fosters a collaborative environment.
Monitoring and Controlling: Staying on Track
The monitoring and controlling phase is essential for ensuring that the project remains aligned with its objectives. It involves continuous oversight to measure performance and apply necessary adjustments.
- Performance Measurement and Reporting: Regularly assessing project progress is crucial. Reports keep stakeholders informed about current status, resource utilization, and timeline adherence. Studies show that projects with consistent performance monitoring are 28% more likely to meet their goals on time.
- Quality Control and Risk Management: Implementing quality control measures ensures that deliverables meet the required standards. Risk management strategies help identify potential issues early, allowing the team to mitigate them before they escalate.
Adjustments and corrective actions are sometimes needed to address deviations from the plan. By analyzing performance data, project managers can make informed decisions to steer the project back on course. Whether it’s reallocating resources or revising timelines, these actions are vital for maintaining momentum and achieving success.
Incorporating these practices during the monitoring and controlling phase not only safeguards the project’s progress but also enhances the team’s ability to deliver quality outcomes.
Closure: Wrapping Up the Project
Final Deliverables
The closure phase is where all project deliverables are finalized and handed over for client acceptance. This involves ensuring that every component meets the agreed-upon standards and is ready for use. Acceptance from stakeholders signifies the successful completion of project objectives, paving the way for a smooth transition from development to operational use.
Post-project Evaluation
Conducting a thorough post-project evaluation is crucial to assess the project’s overall success and effectiveness. This evaluation involves reviewing performance against initial goals, budget, and timelines. Gathering feedback from team members and stakeholders offers valuable insights into both successes and areas for improvement.
Lessons Learned
Documenting lessons learned is an essential step for continuous improvement. It involves capturing insights and experiences that can benefit future projects. This documentation serves as a reference point, helping teams avoid past mistakes and replicate successful strategies.
- Ensure all deliverables meet quality standards.
- Obtain formal acceptance from stakeholders.
- Conduct a detailed post-project evaluation.
- Document lessons learned for future reference.
Wrapping up the project meticulously ensures that the efforts invested yield lasting benefits and lay the groundwork for future success.
Common Challenges in Project Management
Even with a well-structured approach to project management, challenges can arise that threaten the success of a project. Understanding these common hurdles can help project managers stay proactive and prepared.
- Scope Creep and Changing Requirements: One of the most prevalent challenges is scope creep, where a project’s scope expands beyond its original objectives. This often occurs due to unplanned changes in requirements, leading to increased costs and extended timelines. According to a PMI study, 52% of projects experience scope creep, impacting their overall success.
- Resource Constraints: Limited resources, whether financial, human, or material, can severely hinder project progress. Efficient resource allocation is critical, as shortages can lead to bottlenecks and delays, compromising the project’s quality and delivery.
- Communication Breakdowns: Effective communication is essential for project success, yet breakdowns are common. Miscommunication can lead to misunderstandings, errors, and conflicts among team members and stakeholders. Establishing clear communication channels and protocols is vital to mitigate this risk.
By recognizing these challenges early, project managers can devise strategies to address them, ensuring that projects remain on track and achieve their desired outcomes.
Best Practices for Successful Project Management
Ensuring the success of a project requires adhering to several best practices that promote efficiency and effectiveness throughout each phase.
- Effective Communication: Clear communication is the backbone of project success. Establishing regular updates and feedback sessions helps keep everyone informed and aligned. For example, in a software development project, daily stand-up meetings can ensure that the team addresses issues promptly and maintains momentum.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involving stakeholders early and often is crucial. Their input can provide valuable insights and foster a sense of ownership. Consider a construction project where regular meetings with community leaders ensure that local needs and concerns are integrated into the project plan.
- Continuous Learning and Adaptation: Projects often encounter unexpected changes. Encouraging a culture of learning and flexibility allows teams to adapt swiftly. A marketing campaign, for instance, might pivot its strategy based on real-time consumer feedback, ensuring relevance and effectiveness.
By integrating these practices, project managers can navigate complexities more smoothly, leading to successful project outcomes that meet or exceed expectations.
FAQ: Your Project Management Queries Answered
In the world of project management, questions often arise. Here, we address some of the most common queries to help you navigate your projects smoothly.
Q: How can I estimate project timelines effectively?
A: Start by breaking the project into smaller tasks and estimating the time for each. Use historical data from similar projects to guide your estimates and always account for potential delays.
Q: What are the key roles in a project team?
A: Common roles include the project manager, who oversees the project; team members, who execute tasks; and stakeholders, who have an interest in the project’s outcome. Each role is crucial for success.
Q: How can new project managers ensure project success?
A: New managers should focus on clear communication, setting realistic goals, and fostering a collaborative team environment. Continuous learning and seeking mentorship can also be invaluable.
Understanding these aspects can greatly enhance your effectiveness in project management, ensuring that projects are delivered on time and with the desired quality.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In wrapping up our exploration of the key phases of project management, it’s clear that each stage, from initiation through to closure, plays a crucial role in ensuring project success. By setting a solid foundation in the initiation phase, creating a detailed plan, effectively executing tasks, vigilantly monitoring progress, and closing with thorough evaluation, projects are more likely to meet their objectives.
Following these structured phases is essential as it brings order, clarity, and efficiency to the project management process. It helps teams navigate challenges and adapt to changes with agility.
As you dive into future projects, embrace these insights as your guiding framework. With dedication and strategic application, you have the power to transform ideas into successful project outcomes.